Why Robots Struggle To Replicate The Craftsmanship Of Nike Shoes
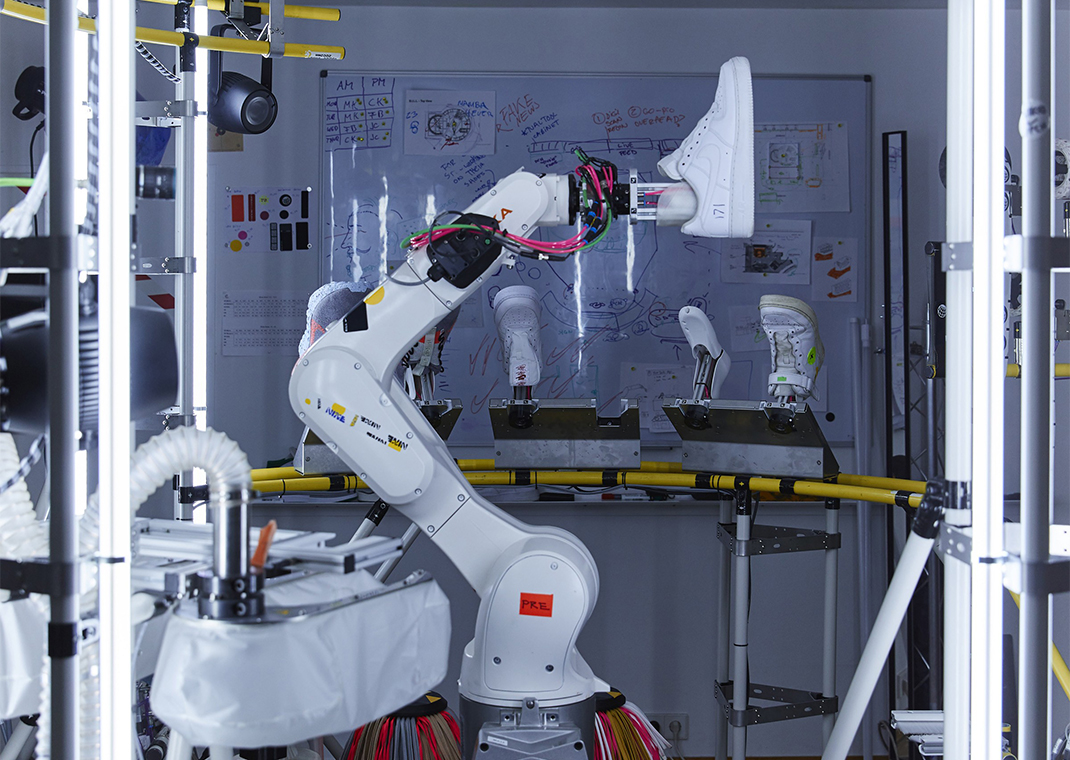

Table of Contents
The Intricacies of Nike Shoe Construction
The seemingly simple act of creating a Nike shoe involves a surprisingly complex interplay of materials and techniques. This complexity significantly challenges the capabilities of current robotic systems.
Complex Stitching and Material Layering
Nike shoes utilize a variety of materials and innovative stitching techniques, such as Flyknit, which creates a seamless, sock-like upper, and the intricate layering found in Air Max models. These require a level of precision and artistry that is difficult, if not impossible, to perfectly replicate robotically.
- Challenges in robotic replication:
- Precise stitching control: Robots struggle with the nuanced adjustments needed to maintain consistent tension and stitch quality across varying material thicknesses and textures. Human hands intuitively adapt to these variations.
- Material handling: The delicate nature of some materials used in Nike shoes, such as lightweight fabrics and advanced synthetic leathers, presents significant challenges for robotic grippers and manipulation systems.
- Complex 3D shaping: The intricate layering and shaping involved in certain designs require a dexterity and adaptability that robots currently lack.
Hand-finishing and Quality Control
Beyond the initial construction, hand-finishing plays a crucial role in ensuring the high-quality standards associated with Nike shoes. Human inspectors possess the experience and subtle judgment to identify imperfections that automated systems often miss.
- Challenges in automated quality control:
- Subtle imperfections: Robots struggle to detect minor inconsistencies in stitching, adhesive application, or material flaws that a human eye can quickly identify.
- Overall feel and comfort: Assessing the overall comfort and feel of a shoe is a subjective judgment based on human experience, a quality currently beyond the capabilities of automated systems.
- Cost-prohibitive perfection: Achieving truly flawless robotic quality control would likely require an extremely high level of investment in sophisticated sensors and AI algorithms, making it economically unviable.
The Limitations of Current Robotic Technology
While robotics in shoe manufacturing is improving, several key limitations prevent robots from fully replicating the craftsmanship of Nike shoes.
Dexterity and Adaptability
Current robotic systems lack the dexterity and adaptability of human hands. Many tasks involved in shoemaking require fine motor skills and the ability to adjust techniques based on the specific material or situation.
- Limitations in dexterity:
- Precise placement of small components: Robots struggle with placing small components with the accuracy and precision that a human hand can achieve.
- Handling irregular materials: Variations in material consistency and shape pose challenges to the rigid programming of robotic systems.
- Lack of improvisation: Human workers can often improvise and adjust their techniques on the fly, a capacity robots lack.
Sensory Feedback and Decision-Making
Human workers use sensory feedback (sight, touch, and even sound) to make crucial decisions during the shoemaking process. Robots currently lack this sophisticated level of sensory input and the ability to use it to adjust their actions.
- The human advantage:
- Adjusting stitch tension: Skilled workers adjust stitching tension based on the material’s feel, ensuring optimal strength and appearance. Robots lack this capacity for real-time sensory adjustment.
- Identifying material defects: Experienced workers can detect subtle flaws in materials that might be missed by automated systems.
- AI and sensory development: Research is ongoing to develop robotic tactile sensors and AI-driven decision-making systems that mimic this human capability, but we’re still a long way from achieving true parity.
The Economic and Social Implications
The shift towards robotic shoe manufacturing carries significant economic and social consequences.
Cost of Automation
Implementing advanced robotics in shoe manufacturing requires substantial upfront investment and ongoing maintenance costs. These costs need to be weighed against the cost of employing skilled human labor.
- Economic considerations:
- High initial investment: Robotic systems are significantly more expensive than human labor in the short term.
- Ongoing maintenance and repairs: Robots require regular maintenance and repairs, adding to the overall cost.
- Potential job displacement: The widespread adoption of robotic systems in shoe manufacturing could lead to job losses in the industry.
The Value of Human Craftsmanship
Despite the drive toward automation, there's a growing appreciation for hand-made goods and the unique value they offer. This creates a niche market for genuinely handcrafted, high-quality shoes.
- Marketing and consumer demand:
- Premium pricing: Handcrafted shoes can command premium prices, appealing to consumers who value quality and authenticity.
- Sustainable practices: Combining automation with human craftsmanship allows for more sustainable manufacturing methods, focusing on smaller batches and reduced waste.
- Preserving traditional skills: Maintaining human craftsmanship in shoemaking safeguards valuable traditional skills and expertise.
Conclusion
Replicating the intricate craftsmanship of Nike shoes with robots presents significant challenges. The dexterity, adaptability, and sensory feedback employed by skilled human workers remain difficult to replicate with current technology. While robotic shoemaking will continue to evolve, the human touch—and the value it brings—appears likely to remain an essential part of the high-end shoemaking process for the foreseeable future. Will robots ever truly replicate the unique craftsmanship that makes Nike shoes iconic, or will the human touch always remain essential in the future of Nike shoe manufacturing and robotic shoemaking in general?

Featured Posts
-
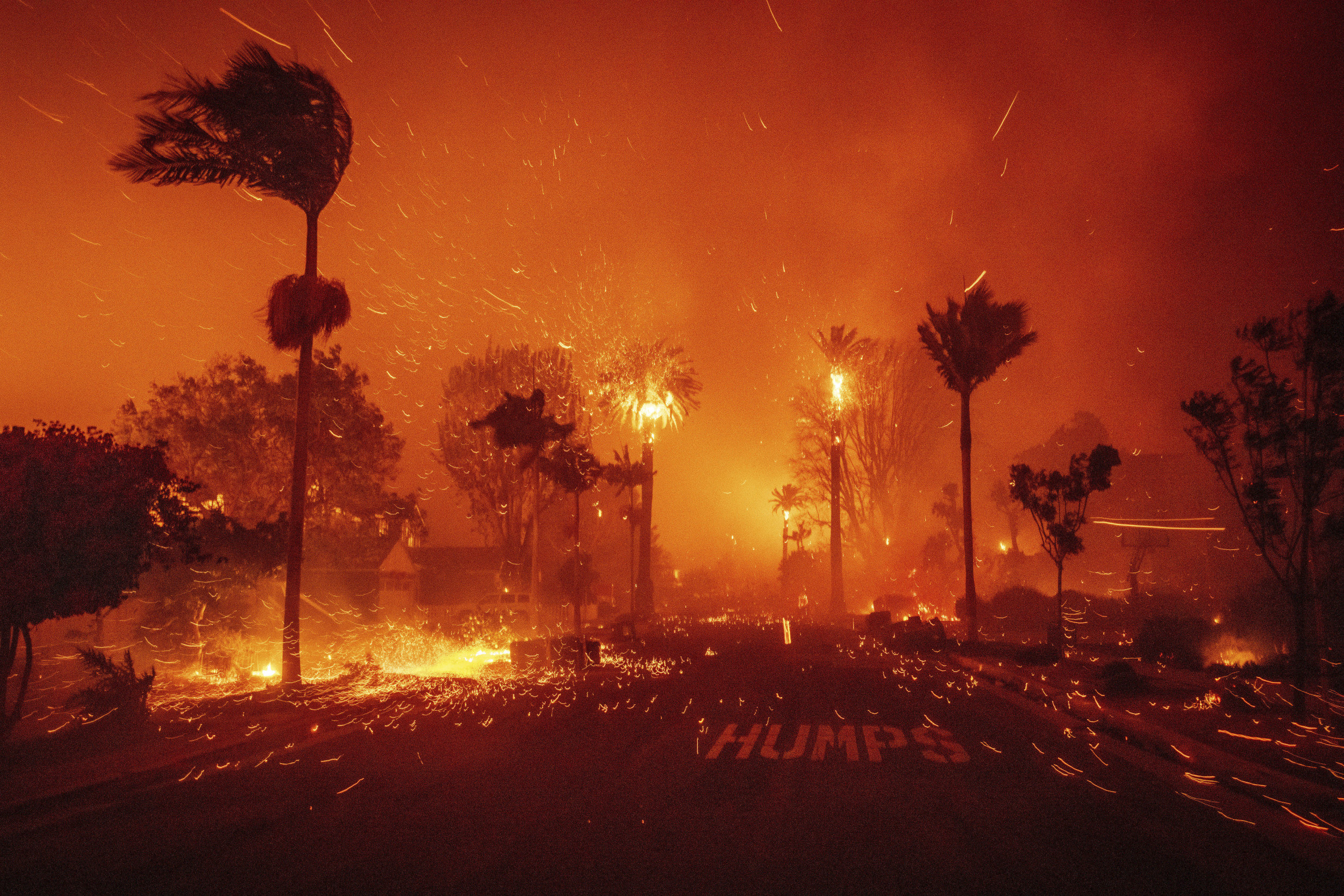 California Wildfires Impact On Celebrities In The Palisades
Apr 22, 2025
California Wildfires Impact On Celebrities In The Palisades
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Joint Security Initiatives China And Indonesia Collaborate
Apr 22, 2025
Joint Security Initiatives China And Indonesia Collaborate
Apr 22, 2025 -
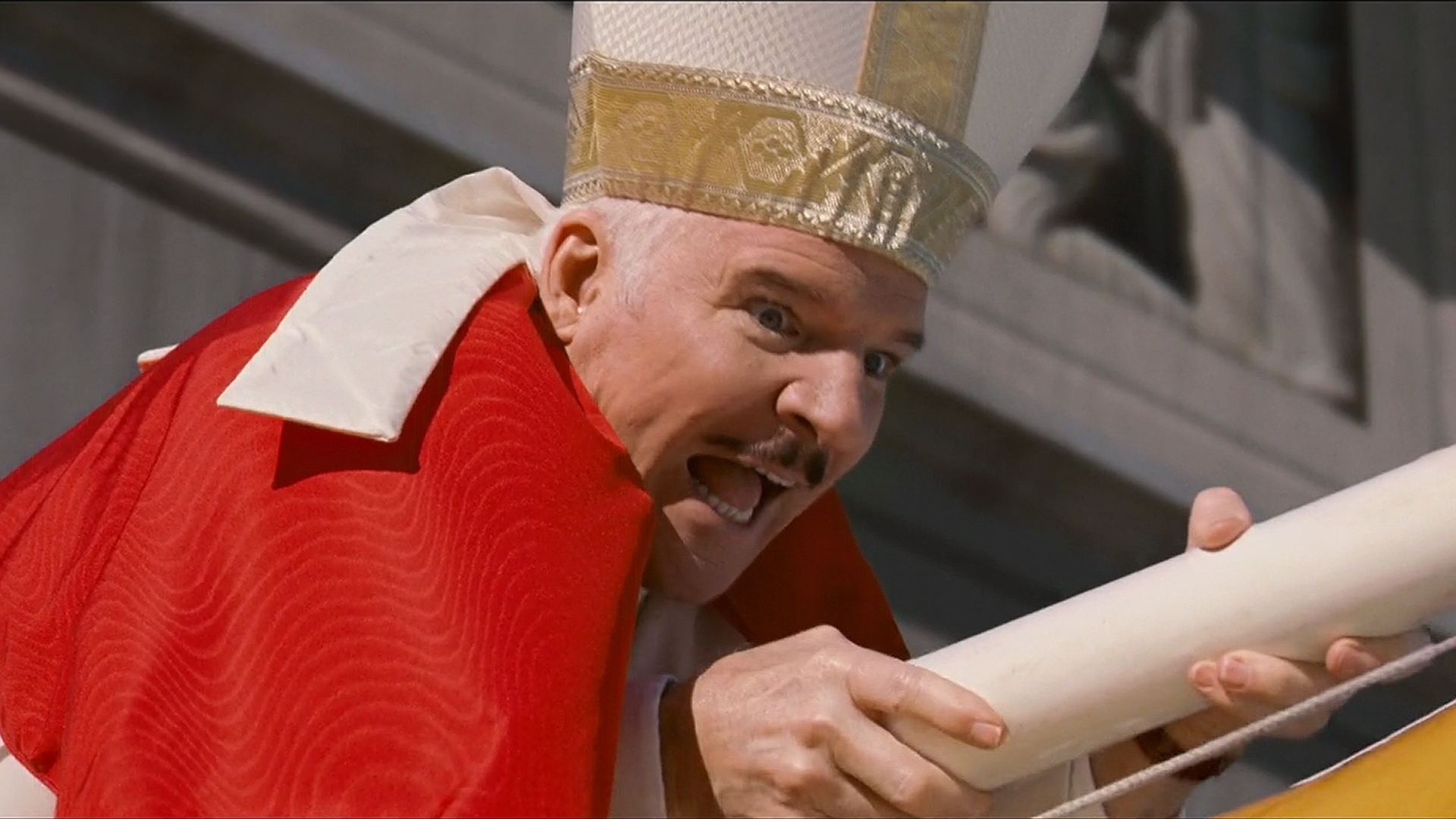 The Next Pope How Franciss Papacy Will Shape The Conclave
Apr 22, 2025
The Next Pope How Franciss Papacy Will Shape The Conclave
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Search Monopoly Case Google And Doj Head Back To Court
Apr 22, 2025
Search Monopoly Case Google And Doj Head Back To Court
Apr 22, 2025 -
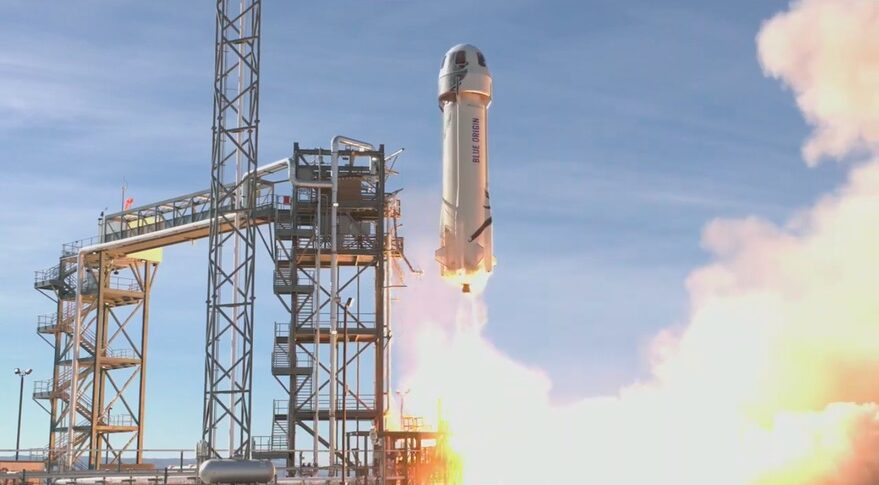 Vehicle Subsystem Issue Forces Blue Origin Launch Cancellation
Apr 22, 2025
Vehicle Subsystem Issue Forces Blue Origin Launch Cancellation
Apr 22, 2025
