China's Growth Model At Risk: Analyzing The Tariff Threat

Table of Contents
The Current State of China's Economy and its Dependence on Exports
China's economic growth model has long been export-oriented, heavily reliant on global trade for sustained expansion. This dependence on exports has fueled impressive GDP growth for decades, but it also creates significant vulnerabilities to external shocks, such as trade wars and tariff impositions. China's success hinges on its ability to produce and export a vast range of goods at competitive prices. This dependence on exports is a double-edged sword—a source of strength and a potential weakness impacting China's growth model.
- Key export sectors and their contribution to GDP: Electronics, textiles, machinery, and toys are major contributors, forming a significant portion of China's GDP. The manufacturing sector, especially, plays a crucial role in China’s export-driven economy.
- Major trading partners and their importance to China's economy: The United States, European Union, and ASEAN countries are key trading partners, with their markets crucial for absorbing Chinese exports. Disruptions in these relationships directly affect China's economic health.
- Current economic indicators (GDP growth, inflation, etc.) and their trends: While China's GDP growth has slowed in recent years, it remains relatively robust. However, rising inflation and uncertainties related to the tariff threat pose challenges to sustaining this growth. The current economic indicators require careful monitoring in the context of the tariff threat to accurately assess the impact on China's growth model.
This export-led growth model, while highly successful, makes China's economy exceptionally vulnerable to external factors like trade wars and tariffs. The imposition of tariffs can significantly disrupt export flows, impacting both production and employment.
The Impact of Tariffs on Chinese Industries
The tariff threat has had a tangible impact on several key Chinese industries. The technology sector, in particular, has been significantly affected by trade restrictions. Manufacturing, a cornerstone of China's economy, has also experienced substantial disruption. Furthermore, agricultural products have faced increasing challenges in accessing foreign markets. The repercussions of these impacts on China's growth model are far-reaching.
- Examples of tariffs imposed and their effects on specific industries: Tariffs on Chinese electronics and manufactured goods have led to increased prices for consumers and reduced market share for Chinese companies. This has affected not only profitability, but also the image of Chinese goods on the global market.
- Analysis of job losses and economic disruptions due to tariffs: The impact of tariffs has resulted in job losses in affected industries, particularly in manufacturing and related sectors. Economic disruptions have been observed across various supply chains.
- Countermeasures adopted by Chinese businesses to mitigate the impact of tariffs: Chinese businesses have adopted various countermeasures including diversification of export markets, exploring new technologies, and increasing domestic consumption. Yet, this is no easy fix, as the effects of the tariffs on China's growth model are ongoing and complex.
The potential for retaliatory tariffs further compounds the problem, creating a cascading effect that disrupts global supply chains and negatively impacts overall economic growth. The interplay between tariffs and retaliation poses a serious threat to China's growth model.
Alternative Growth Strategies for China Amidst the Tariff Threat
To mitigate the risks associated with the tariff threat, China needs to diversify its economy and reduce its reliance on exports. This requires a strategic shift towards alternative growth strategies.
- Investment in domestic consumption and services: Boosting domestic consumption can reduce dependence on external markets and stimulate internal growth. This involves creating a middle class with higher purchasing power.
- Technological innovation and upgrading industries: Investing in research and development, fostering innovation, and upgrading industries can make Chinese products more competitive and less vulnerable to tariffs. Emphasis should be placed on innovation and technological dominance.
- Development of a more robust domestic supply chain: Reducing reliance on foreign components and building a more resilient domestic supply chain can lessen the impact of external shocks. This requires a strategy of localized sourcing and increased self-sufficiency.
- Focus on sustainable and green technologies: Investing in sustainable and green technologies can open up new export markets and position China as a leader in this growing sector.
The successful implementation of these strategies will be critical in ensuring the long-term stability and sustainability of China's growth model in the face of the tariff threat. These strategies can reduce the reliance on volatile export markets and provide resilience to the nation's economy.
Geopolitical Implications of the Tariff Threat to China's Growth Model
The tariff threat has far-reaching geopolitical implications, impacting global trade, supply chains, and international relations.
- Impact on global supply chains and international trade: Trade tensions between China and other countries disrupt global supply chains, increasing uncertainty and costs for businesses worldwide.
- Shifting geopolitical alliances and power dynamics: The tariff threat is reshaping global power dynamics and influencing alliances between countries.
- Potential for increased regional instability: Increased trade friction can lead to regional instability and exacerbate existing geopolitical tensions.
The tariff threat significantly impacts China's international relations and its role in the global economy. China’s response to these challenges and its ability to successfully navigate these geopolitical headwinds will be crucial in shaping the future of its growth model.
Conclusion: The Future of China's Growth Model in the Face of Tariff Threats
The analysis reveals significant risks posed by tariffs to China's growth model. The nation's heavy reliance on exports makes it vulnerable to external shocks, and the ongoing trade tensions underscore the urgent need for diversification. The long-term success of China's economic future hinges on its ability to successfully implement alternative growth strategies, fostering domestic consumption, technological innovation, and a more robust domestic supply chain. Addressing the tariff threat requires a multifaceted approach, incorporating economic reforms, strategic technological advancements, and a nuanced approach to international relations.
Understanding the complexities of China's growth model and the ongoing tariff threat is crucial for navigating the future of global economics. Further research and proactive policy adjustments are vital to mitigating risks and securing a stable, sustainable economic future for China. The challenges posed by the tariff threat necessitate a proactive and adaptive approach to ensure the continued prosperity of China's economic growth. Addressing the tariff impacts and securing China's economic future requires innovative thinking and strategic planning.

Featured Posts
-
 Following The Karen Read Murder Case A Comprehensive Timeline
Apr 22, 2025
Following The Karen Read Murder Case A Comprehensive Timeline
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Debate Erupts Over Fsus Decision To Resume Classes Following Tragedy
Apr 22, 2025
Debate Erupts Over Fsus Decision To Resume Classes Following Tragedy
Apr 22, 2025 -
 The Automotive Market In China Case Studies Of Bmw And Porsches Challenges
Apr 22, 2025
The Automotive Market In China Case Studies Of Bmw And Porsches Challenges
Apr 22, 2025 -
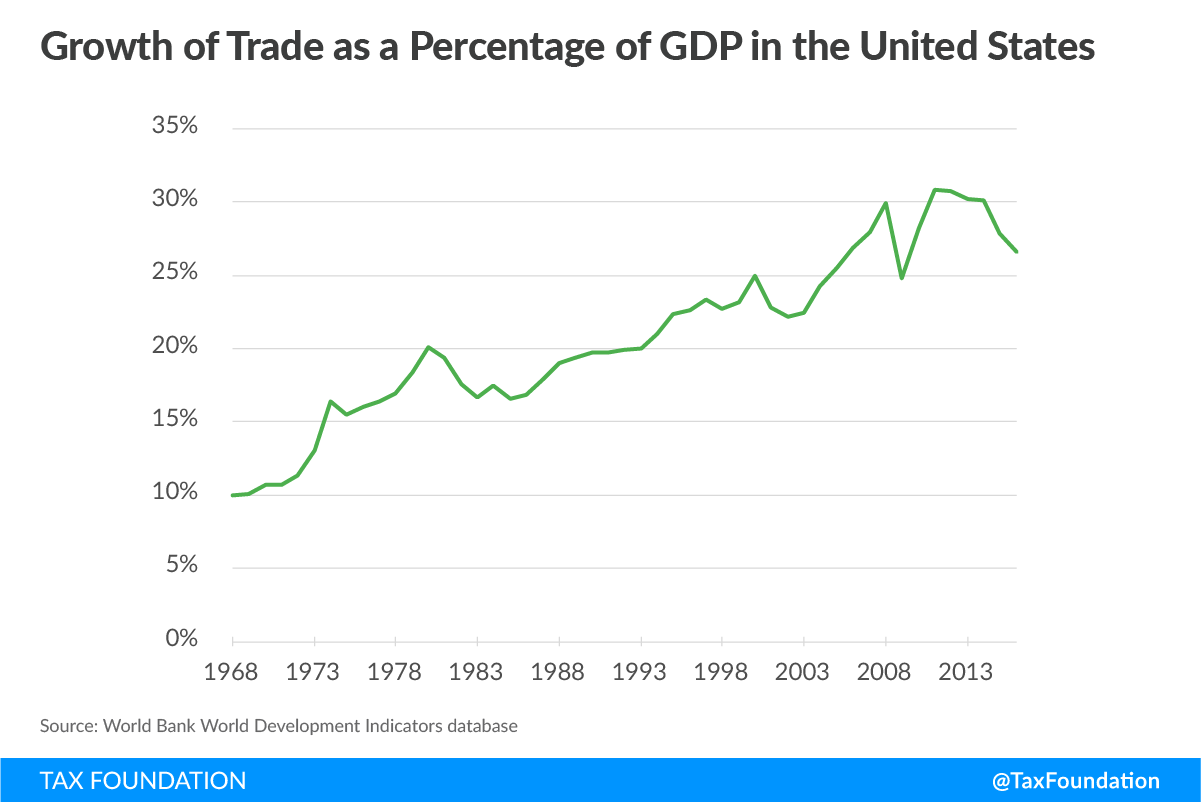 Trump Tariffs How Businesses Use Tik Tok To Find Solutions
Apr 22, 2025
Trump Tariffs How Businesses Use Tik Tok To Find Solutions
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Trump Administration To Withdraw 1 Billion More In Funding From Harvard
Apr 22, 2025
Trump Administration To Withdraw 1 Billion More In Funding From Harvard
Apr 22, 2025
